BWA2.0은 1MHz에 이르는 주파수와 2중 클램프 전극을 활용하여 세포내수분,
세포외수분, 분위별 체수분량 등을 정확하게 측정하고, 체수분 균형 및 영양 상태 판단, 건체중 결정의 참고 지표를 제공합니다.
APPLICATION
Medical Approved
APPLICATION
Body Water Analyzer
MEDICAL
Nephrology
InBody devices are non-invasive and tests are completed in less than 60 seconds. InBody data can be used to fluctuations and fine tune the process of bringing dialysis patients to the appropriate dry weight. InBody devices can also be used to determine where a patient is holding excess water and track fluid movement. This accurate, reproducible information doesn’t rely on empirical data and therefore, reflects the patient.
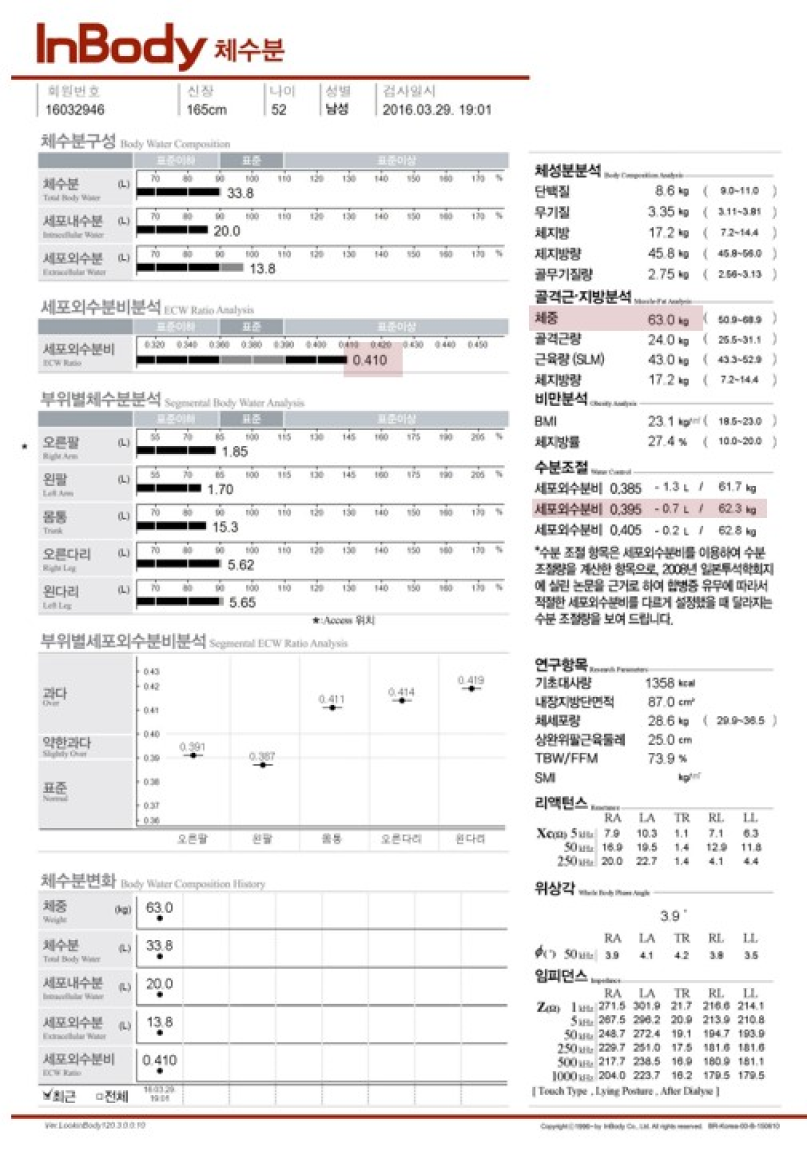
SEGMENTAL ECW/TBW WATER ANALYSIS
Avoid interdialytic complications from fluid accumulation
Interdialytic weight gain can be masked by the loss of muscle and fat mass. Professionals rely on the indirect practice of pitting edema to identify changes in fluid levels. Objective measures of body water help identify water retention as a form of weight change independent of changes in muscle or fat mass.
Nephrologists can use Segmental ECW/TBW Analysis to distinguish fluid accumulation from muscle and fat composition, allowing for more accurate
tracking of fluid overload independent of nutritional status.
This will allow physicians to set proper goal weights, confirm fluid volumes post-dialysis, and make more appropriate adjustments of patient goal weights long-term.

Interdialytic weight gain can be masked by the loss of muscle and fat mass. Professionals rely on the indirect practice of pitting edema to identify changes in fluid levels. Objective measures of body water help identify water retention as a form of weight change independent of changes in muscle or fat mass.
Nephrologists can use Segmental ECW/TBW Analysis to distinguish fluid accumulation from muscle and fat composition, allowing for more accurate
tracking of fluid overload independent of nutritional status.
This will allow physicians to set proper goal weights, confirm fluid volumes post-dialysis, and make more appropriate adjustments of patient goal weights long-term.
